The sample tables used in the following examples are:-
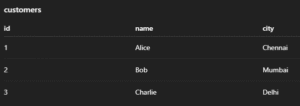
1. Customer Table
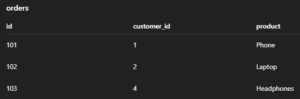
2. Order Table
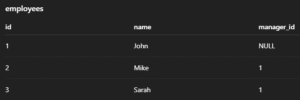
3. Employee Table
4. Department Table
5. Marks Table

6. Student Table
1. INSERT INTO – Add New Records
Inserts new rows into a table. Values can be inserted into all or selected columns.
Syntax:
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...)
VALUES (value1, value2, ...);Example:
INSERT INTO students (id, name, age) VALUES (1, 'Arun', 20);Output:

2. INSERT IGNORE – Skip Duplicates Silently
Inserts data but skips the row if it violates uniqueness constraints like PRIMARY KEY.
Syntax:
INSERT IGNORE INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...)
VALUES (value1, value2, ...);Example:
INSERT IGNORE INTO students (id, name) VALUES (1, 'Arun');Output:

3. INSERT … ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE – Upsert
If a duplicate key is found, updates the row instead of inserting a new one.
Syntax:
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2)
VALUES (value1, value2)
ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE column2 = new_value;Example:
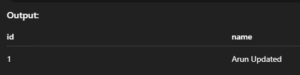
INSERT INTO students (id, name) VALUES (1, 'Arun')
ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE name = 'Arun Updated';Output:
4. SELECT – Read Data from Table
Retrieves data from one or more tables. You can select specific columns or all (*).
Syntax:
SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name;
-- OR
SELECT * FROM table_name;Example:
SELECT name, age FROM students;Output:

5. SELECT DISTINCT – Avoid Duplicate Rows
Returns only unique records from the selected column(s).
Syntax:
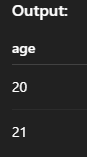
SELECT DISTINCT column_name FROM table_name;Example:
SELECT DISTINCT age FROM students;Output:
6. SELECT WHERE – Conditional Read
Filters records based on a given condition.
Syntax:
SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name WHERE condition;Example:
SELECT * FROM students WHERE age > 18;Output:
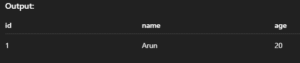
7. SELECT ORDER BY – Sort Results
Sorts the output in ascending (ASC) or descending (DESC) order.
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM table_name ORDER BY column_name ASC|DESC;Example:
SELECT * FROM students ORDER BY age DESC;Output:
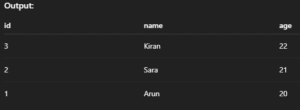
8. SELECT LIMIT – Limit Output Rows
Fetches only a fixed number of rows from the result.
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM table_name LIMIT number_of_rows;Example:
SELECT * FROM students LIMIT 5;Output:
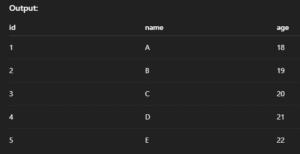
9. SELECT LIKE – Pattern Matching
Finds rows where column values match a specific pattern using % or _.
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE column_name LIKE 'pattern';Example:
SELECT * FROM students WHERE name LIKE 'A%';Output:

10. UPDATE – Change Existing Data
Updates values in one or more columns for selected rows.
Syntax:
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2
WHERE condition;Example:
UPDATE students SET age = 21 WHERE id = 1;Output:

11. UPDATE with JOIN – Modify Using Related Tables
Allows updates based on matching rows in other tables.
Syntax:
UPDATE table1
JOIN table2 ON table1.column = table2.column
SET table1.column_to_update = value
WHERE condition;Example:
UPDATE orders o
JOIN customers c ON o.customer_id = c.id
SET o.status = 'Confirmed'
WHERE c.city = 'Chennai';Output:
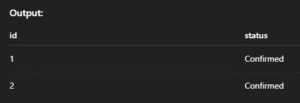
12. DELETE – Remove Data from Table
Deletes rows matching a condition from a table.
Syntax:
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;Example:
DELETE FROM students WHERE id = 1;Output:
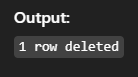
13. DELETE with JOIN – Delete from Multiple Tables
Allows deleting rows based on matching conditions in another table.
Syntax:
DELETE alias1 FROM table1 AS alias1
JOIN table2 AS alias2 ON alias1.column = alias2.column
WHERE condition;Example:
DELETE s FROM students s
JOIN dropped_list d ON s.id = d.student_id;Output:
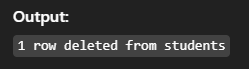
14. REPLACE INTO – Insert or Replace Row
Inserts a row or replaces the existing row with the same primary key.
Syntax:
REPLACE INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, ...);Example:
REPLACE INTO students (id, name) VALUES (1, 'New Name');Output:

15. TRUNCATE – Delete All Data (Preserve Table)
Removes all rows from a table quickly but keeps its structure.
Syntax:
TRUNCATE TABLE table_name;Example:
TRUNCATE TABLE students;Output:
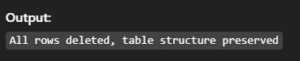
16. SELECT INTO OUTFILE – Export Query Result to File
Saves the result of a SELECT query into a file on the server.
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM table_name INTO OUTFILE '/path/to/file.csv';Example:
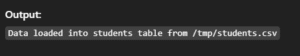
SELECT * FROM students INTO OUTFILE '/tmp/students.csv';Output:
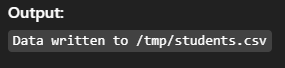
17. LOAD DATA INFILE – Import Data from File
Loads data from a file directly into a MySQL table.
Syntax:
LOAD DATA INFILE '/path/to/file.csv' INTO TABLE table_name
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',' ENCLOSED BY '"' LINES TERMINATED BY 'n';Example:
LOAD DATA INFILE '/tmp/students.csv' INTO TABLE students;Output: