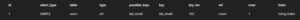EXPLAIN shows how MySQL executes a query — whether it uses indexes, how many rows it scans, and which table joins happen.
General Syntax:
EXPLAIN SELECT name FROM users WHERE email = ‘test@example.com’;
Example:-
Step 1: Create a Sample Table and Insert Data
CREATE TABLE users (
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(100),
email VARCHAR(100)
);
INSERT INTO users (name, email) VALUES
(‘Arun’, ‘arun@example.com’),
(‘Riya’, ‘riya@example.com’),
(‘Test User’, ‘test@example.com’);
Step 2: Run the Query with EXPLAIN
EXPLAIN SELECT name FROM users WHERE email = ‘test@example.com’;
Expected Output:-
 (This will get slower as table size increases.)
(This will get slower as table size increases.)
Step 3: Optimize by Creating an Index
CREATE INDEX idx_email ON users(email);
Step 4: Run the EXPLAIN Again
EXPLAIN SELECT name FROM users WHERE email = ‘test@example.com’;
Output:-