Types of Linked Lists
Depending on how the nodes are connected, linked lists are classified into three types:
A. Singly Linked List
A Singly Linked List is the simplest type of linked list. In this structure, each node contains data and a reference (pointer) to the next node in the sequence. The last node points to null, indicating the end of the list. 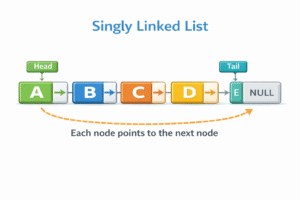
Key Characteristics:
- Unidirectional: You can only traverse the list in one direction (Head $\to$ Tail). You cannot go back to the previous node.
- Memory Efficient: It requires less memory per node compared to a doubly linked list because it only stores one pointer.
Java Node Structure
As seen in your Stack implementation, the node for a singly linked list is defined with just data and next :
class Node {
int data;
Node next; // Reference to the next node
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null; // Ends with null by default [cite: 179, 766]
}
}
- Navigation: Forward only.
- Memory: Uses less memory (only one pointer per node).
- Analogy: A conga line where everyone holds the waist of the person in front.
B. Doubly Linked List
A Doubly Linked List is a more complex structure where each node contains three parts instead of two. It allows traversal in both directions.
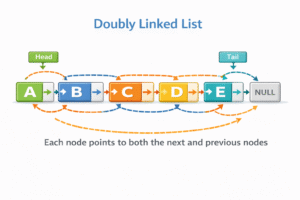
Node Architecture:
- Prev: A pointer to the previous node.
- Data: The value stored.
- Next: A pointer to the next node.
Java Implementation
The Node class expands to include the prev pointer.
class DoublyNode {
int data;
DoublyNode next;
DoublyNode prev; // New pointer for backward navigation
public DoublyNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
public class DoublyLinkedList {
DoublyNode head;
// Insert at the beginning
public void push(int data) {
DoublyNode newNode = new DoublyNode(data);
newNode.next = head; // 1. New node points to current head
newNode.prev = null; // 2. New node's prev is null (it's new head)
if (head != null) {
head.prev = newNode; // 3. Old head's prev points to new node
}
head = newNode; // 4. Update head
}
}
Advantages vs. Disadvantages
- Pros: Can traverse both ways. Deletion is easier because you have access to the previous node immediately.
- Cons: Consumes more memory (extra pointer). Code is slightly more complex to maintain (must update two pointers for every insertion/deletion).
Real-Life Analogy
Web Browser History: You can click “Back” to go to the previous page (prev pointer) or “Forward” to go to the next page (next pointer). The browser maintains a link in both directions.
C. Circular Linked List
A Circular Linked List is a variation where the list has no end. The last node’s next pointer, instead of pointing to null, points back to the Head (first node). This forms a continuous loop. 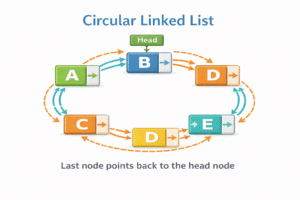
Types of Circular Lists:
- Circular Singly Linked List: Simple nodes, but the tail connects to the head.
- Circular Doubly Linked List: Doubly nodes, where tail connects to head and head connects to tail.
Java Logic (Singly Circular)
Notice that we never set next to null.
public class CircularLinkedList {
Node head = null;
Node tail = null;
public void add(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
// If list is empty, point head to new node
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
newNode.next = head; // Point back to itself
} else {
// Standard insertion
tail.next = newNode; // Old tail points to new node
tail = newNode; // Update tail
tail.next = head; // **CRITICAL**: New tail points back to Head
}
}
// Traversal requires a do-while loop to avoid infinite loops
public void display() {
if (head == null) return;
Node current = head;
do {
System.out.print(current.data + " -> ");
current = current.next;
} while (current != head); // Stop when we return to start
System.out.println("(Head)");
}
}
Real-Life Analogy
- Monopoly Board Game: The board is a continuous loop. After the last space (Boardwalk), you move right back to the first space (Go).
- Music Playlist (Repeat All): When the last song finishes, the player automatically starts the first song again.
Comparison Table for Your Course
| Feature | Singly Linked List | Doubly Linked List | Circular Linked List |
| Direction | Forward Only | Forward & Backward | Forward (Loops back) |
| Memory | Low (1 pointer) | High (2 pointers) | Low (1 pointer) |
| Insertion | Fast | Moderate (more pointers to update) | Fast |
| End of List | Points to null | Points to null | Points to Head |
| Best Use | Simple stacks/queues | Music players, Undo/Redo | CPU Scheduling, Games |
