Linked List
A Linked List is a linear data structure where elements are not stored in contiguous memory locations (unlike Arrays). Instead, the elements are linked together using pointers (references).
The Architecture: What is a Node?
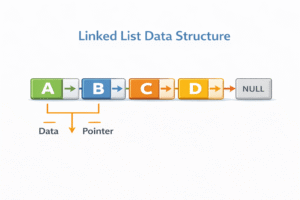
Every element in a linked list is called a Node. Each node has two parts:
- Data: The actual value (e.g., an Integer, String, or Object).
- Next: A reference (or pointer) to the next node in the sequence.
The first node is called the Head. The last node points to null, indicating the end of the list.
Real-World Analogy: The Treasure Hunt
Imagine a treasure hunt. You don’t have a map of all locations at once (like an Array). Instead, you start at the first location (Head). There, you find a clue (Data) and a note telling you where to go next (Pointer). You keep following the clues one by one until you reach the end.
Why use Linked Lists?
- Dynamic Size: It can grow and shrink at runtime. You don’t need to declare a fixed size like an array.
Efficient Insertion/Deletion: You can add or remove items without shifting all other elements (just update the pointers).
