B-Trees
A B-Tree is a self-balancing search tree designed for systems that read and write large blocks of data, like databases and file systems.
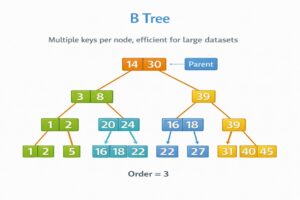
Properties of B-Tree of order M
- Every node has at most M children
- Every non-leaf node (except root) has at least ⌈M/2⌉ children
- The root has at least 2 children (if it’s not a leaf)
- All leaves are at the same level
- A non-leaf node with k children contains k-1 keys
B-Tree Implementation (Order 3)
java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class BTreeNode {
List<Integer> keys;
int t; // Minimum degree (minimum number of keys is t-1)
List<BTreeNode> children;
boolean isLeaf;
public BTreeNode(int t, boolean isLeaf) {
this.t = t;
this.isLeaf = isLeaf;
this.keys = new ArrayList<>();
this.children = new ArrayList<>();
}
// Search a key in subtree rooted with this node
BTreeNode search(int key) {
// Find the first key greater than or equal to k
int i = 0;
while (i < keys.size() && key > keys.get(i))
i++;
// If the found key is equal to k, return this node
if (i < keys.size() && keys.get(i) == key)
return this;
// If key is not found and this is a leaf node
if (isLeaf)
return null;
// Go to the appropriate child
return children.get(i).search(key);
}
// Insert a new key in this node
// The node must be non-full when this function is called
void insertNonFull(int key) {
// Initialize index as index of rightmost element
int i = keys.size() - 1;
// If this is a leaf node
if (isLeaf) {
// Add a new key to keys
keys.add(0);
// Find location where new key should be inserted
while (i >= 0 && keys.get(i) > key) {
keys.set(i + 1, keys.get(i));
i--;
}
// Insert the new key at found location
keys.set(i + 1, key);
} else {
// Find the child which is going to have the new key
while (i >= 0 && keys.get(i) > key)
i--;
// Check if the found child is full
if (children.get(i + 1).keys.size() == 2 * t - 1) {
// If the child is full, split it
splitChild(i + 1, children.get(i + 1));
// After split, the middle key goes up and
// child is split into two
if (keys.get(i + 1) < key)
i++;
}
children.get(i + 1).insertNonFull(key);
}
}
// Split the child y of this node
void splitChild(int i, BTreeNode y) {
// Create a new node to store (t-1) keys of y
BTreeNode z = new BTreeNode(y.t, y.isLeaf);
// Copy the last (t-1) keys of y to z
for (int j = 0; j < t - 1; j++)
z.keys.add(y.keys.get(j + t));
// Copy the last t children of y to z
if (!y.isLeaf) {
for (int j = 0; j < t; j++)
z.children.add(y.children.get(j + t));
}
// Reduce the number of keys in y
y.keys.subList(t - 1, y.keys.size()).clear();
// Remove last t children from y
if (!y.isLeaf)
y.children.subList(t, y.children.size()).clear();
// Insert a new child to this node
children.add(i + 1, z);
// Move a key from y to this node
keys.add(i, y.keys.get(t - 1));
y.keys.remove(t - 1);
}
// Traverse all nodes in a subtree rooted with this node
void traverse() {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < keys.size(); i++) {
// If this is not leaf, traverse the subtree before key[i]
if (!isLeaf)
children.get(i).traverse();
System.out.print(keys.get(i) + " ");
}
// Print the subtree rooted with last child
if (!isLeaf)
children.get(i).traverse();
}
}
class BTree {
BTreeNode root;
int t; // Minimum degree
public BTree(int t) {
this.root = null;
this.t = t;
}
// Search a key in this tree
BTreeNode search(int key) {
return (root == null) ? null : root.search(key);
}
// Insert a new key
void insert(int key) {
// If tree is empty
if (root == null) {
root = new BTreeNode(t, true);
root.keys.add(key);
} else {
// If root is full, tree grows in height
if (root.keys.size() == 2 * t - 1) {
BTreeNode s = new BTreeNode(t, false);
// Make old root as child of new root
s.children.add(root);
// Split the old root and move 1 key to the new root
s.splitChild(0, root);
// New root has two children now.
// Decide which of the two children is going to have new key
int i = 0;
if (s.keys.get(0) < key)
i++;
s.children.get(i).insertNonFull(key);
// Change root
root = s;
} else
root.insertNonFull(key);
}
}
// Traverse the tree
void traverse() {
if (root != null)
root.traverse();
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BTree t = new BTree(3); // A B-Tree with minimum degree 3
System.out.println("Inserting elements: 10, 20, 5, 6, 12, 30, 7, 17");
t.insert(10);
t.insert(20);
t.insert(5);
t.insert(6);
t.insert(12);
t.insert(30);
t.insert(7);
t.insert(17);
System.out.println("Traversal of the constructed tree:");
t.traverse();
int k = 6;
BTreeNode result = t.search(k);
System.out.println("\nSearch for key " + k + ": " +
(result != null ? "Found" : "Not Found"));
k = 15;
result = t.search(k);
System.out.println("Search for key " + k + ": " +
(result != null ? "Found" : "Not Found"));
}
}
```
**Output:**
```
Inserting elements: 10, 20, 5, 6, 12, 30, 7, 17
Traversal of the constructed tree:
5 6 7 10 12 17 20 30
Search for key 6: Found
Search for key 15: Not FoundSimplified B-Tree Example (Order 3)
java
class SimpleBTree {
static class Node {
int n; // Current number of keys
int[] keys = new int[3]; // Maximum 2 keys for order 3
Node[] children = new Node[4]; // Maximum 3 children
boolean isLeaf;
Node(boolean isLeaf) {
this.isLeaf = isLeaf;
this.n = 0;
}
void display(String prefix, boolean isTail) {
System.out.print(prefix + (isTail ? "└── " : "├── "));
System.out.print("[");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(keys[i]);
if (i < n - 1) System.out.print(", ");
}
System.out.println("]");
if (!isLeaf) {
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
if (children[i] != null) {
children[i].display(
prefix + (isTail ? " " : "│ "),
i == n
);
}
}
}
}
}
Node root;
SimpleBTree() {
root = new Node(true);
}
void display() {
if (root != null) {
System.out.println("B-Tree Structure:");
root.display("", true);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleBTree tree = new SimpleBTree();
// Manually creating a simple B-Tree for demonstration
tree.root = new Node(false);
tree.root.keys[0] = 30;
tree.root.n = 1;
tree.root.children[0] = new Node(true);
tree.root.children[0].keys[0] = 10;
tree.root.children[0].keys[1] = 20;
tree.root.children[0].n = 2;
tree.root.children[1] = new Node(true);
tree.root.children[1].keys[0] = 40;
tree.root.children[1].keys[1] = 50;
tree.root.children[1].n = 2;
tree.display();
}
}