AVL Trees
AVL Tree (named after inventors Adelson-Velsky and Landis) is a self-balancing Binary Search Tree where the difference between heights of left and right subtrees (Balance Factor) cannot be more than 1 for any node.
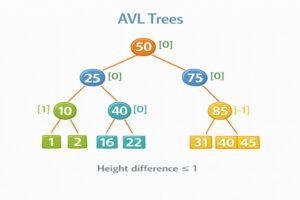
Balance Factor
Balance Factor (BF) = Height(Left Subtree) – Height(Right Subtree)
For AVL tree: BF ∈ {-1, 0, 1}
AVL Tree Implementation
java
class AVLNode {
int data, height;
AVLNode left, right;
AVLNode(int d) {
data = d;
height = 1;
}
}
class AVLTree {
AVLNode root;
// Get height of node
int height(AVLNode node) {
if (node == null)
return 0;
return node.height;
}
// Get maximum of two integers
int max(int a, int b) {
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
// Get balance factor of node
int getBalance(AVLNode node) {
if (node == null)
return 0;
return height(node.left) - height(node.right);
}
// Right rotate subtree rooted with y
AVLNode rightRotate(AVLNode y) {
AVLNode x = y.left;
AVLNode T2 = x.right;
// Perform rotation
x.right = y;
y.left = T2;
// Update heights
y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) + 1;
x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) + 1;
// Return new root
return x;
}
// Left rotate subtree rooted with x
AVLNode leftRotate(AVLNode x) {
AVLNode y = x.right;
AVLNode T2 = y.left;
// Perform rotation
y.left = x;
x.right = T2;
// Update heights
x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) + 1;
y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) + 1;
// Return new root
return y;
}
// Insert a key
AVLNode insert(AVLNode node, int key) {
// 1. Perform normal BST insertion
if (node == null)
return new AVLNode(key);
if (key < node.data)
node.left = insert(node.left, key);
else if (key > node.data)
node.right = insert(node.right, key);
else // Duplicate keys not allowed
return node;
// 2. Update height of this ancestor node
node.height = 1 + max(height(node.left), height(node.right));
// 3. Get the balance factor
int balance = getBalance(node);
// 4. If node becomes unbalanced, then there are 4 cases
// Left Left Case
if (balance > 1 && key < node.left.data)
return rightRotate(node);
// Right Right Case
if (balance < -1 && key > node.right.data)
return leftRotate(node);
// Left Right Case
if (balance > 1 && key > node.left.data) {
node.left = leftRotate(node.left);
return rightRotate(node);
}
// Right Left Case
if (balance < -1 && key < node.right.data) {
node.right = rightRotate(node.right);
return leftRotate(node);
}
// Return the unchanged node pointer
return node;
}
// Find node with minimum value
AVLNode minValueNode(AVLNode node) {
AVLNode current = node;
// Loop down to find the leftmost leaf
while (current.left != null)
current = current.left;
return current;
}
// Delete a node
AVLNode deleteNode(AVLNode root, int key) {
// 1. Perform standard BST delete
if (root == null)
return root;
if (key < root.data)
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
else if (key > root.data)
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
else {
// Node with only one child or no child
if ((root.left == null) || (root.right == null)) {
AVLNode temp = null;
if (temp == root.left)
temp = root.right;
else
temp = root.left;
// No child case
if (temp == null) {
temp = root;
root = null;
} else // One child case
root = temp;
} else {
// Node with two children
AVLNode temp = minValueNode(root.right);
root.data = temp.data;
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, temp.data);
}
}
// If tree had only one node
if (root == null)
return root;
// 2. Update height of current node
root.height = max(height(root.left), height(root.right)) + 1;
// 3. Get balance factor
int balance = getBalance(root);
// 4. If unbalanced, fix it
// Left Left Case
if (balance > 1 && getBalance(root.left) >= 0)
return rightRotate(root);
// Left Right Case
if (balance > 1 && getBalance(root.left) < 0) {
root.left = leftRotate(root.left);
return rightRotate(root);
}
// Right Right Case
if (balance < -1 && getBalance(root.right) <= 0)
return leftRotate(root);
// Right Left Case
if (balance < -1 && getBalance(root.right) > 0) {
root.right = rightRotate(root.right);
return leftRotate(root);
}
return root;
}
// Preorder traversal
void preOrder(AVLNode node) {
if (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
}
// Print tree structure
void printTree(AVLNode node, String prefix, boolean isLeft) {
if (node == null)
return;
System.out.println(prefix + (isLeft ? "├── " : "└── ") + node.data);
if (node.left != null || node.right != null) {
if (node.left != null)
printTree(node.left, prefix + (isLeft ? "│ " : " "), true);
else
System.out.println(prefix + (isLeft ? "│ " : " ") + "├── null");
if (node.right != null)
printTree(node.right, prefix + (isLeft ? "│ " : " "), false);
else
System.out.println(prefix + (isLeft ? "│ " : " ") + "└── null");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AVLTree tree = new AVLTree();
/* Constructing tree given in the above figure */
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25);
System.out.println("Preorder traversal of AVL tree:");
tree.preOrder(tree.root);
System.out.println("\n\nTree structure:");
tree.printTree(tree.root, "", false);
System.out.println("\n\nDeleting 10...");
tree.root = tree.deleteNode(tree.root, 10);
System.out.println("Preorder traversal after deletion:");
tree.preOrder(tree.root);
System.out.println("\n\nTree structure after deletion:");
tree.printTree(tree.root, "", false);
}
}
```
**Output:**
```
Preorder traversal of AVL tree:
30 20 10 25 40 50
Tree structure:
└── 30
├── 20
│ ├── 10
│ │ ├── null
│ │ └── null
│ └── 25
│ ├── null
│ └── null
└── 40
├── null
└── 50
├── null
└── null
Deleting 10...
Preorder traversal after deletion:
30 20 25 40 50
Tree structure after deletion:
└── 30
├── 20
│ ├── null
│ └── 25
│ ├── null
│ └── null
└── 40
├── null
└── 50
├── null
└── nullAVL Rotation Examples
java
class AVLRotationExamples {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AVLTree tree = new AVLTree();
System.out.println("=== Left-Left Case (Right Rotation) ===");
System.out.println("Inserting: 30, 20, 10");
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10);
tree.printTree(tree.root, "", false);
tree = new AVLTree();
System.out.println("\n=== Right-Right Case (Left Rotation) ===");
System.out.println("Inserting: 10, 20, 30");
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30);
tree.printTree(tree.root, "", false);
tree = new AVLTree();
System.out.println("\n=== Left-Right Case ===");
System.out.println("Inserting: 30, 10, 20");
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20);
tree.printTree(tree.root, "", false);
tree = new AVLTree();
System.out.println("\n=== Right-Left Case ===");
System.out.println("Inserting: 10, 30, 20");
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20);
tree.printTree(tree.root, "", false);
}
}