Introduction to Binary Search Tree
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a binary tree with a special ordering property that makes searching efficient:
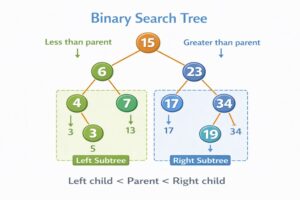
- All nodes in the left subtree have values less than the parent node
- All nodes in the right subtree have values greater than the parent node
- Both left and right subtrees must also be BSTs
- No duplicate values (in standard BST)
Visual Example
Valid BST: Invalid BST:
50 50
/ \ / \
30 70 30 70
/ \ / \ / \ / \
20 40 60 80 20 65 60 80
↑
(65 > 50, should be in right)Why Use BST?
Advantages:
- Efficient searching: O(log n) average case
- Maintains sorted order (inorder traversal gives sorted sequence)
- Dynamic size (can grow/shrink)
- Efficient insertion and deletion
Use Cases:
- Dictionary implementations
- Database indexing
- Priority queues
- Auto-complete features
- File system organization
Properties and Characteristics
1. BST Node Structure
java
class BSTNode {
int data;
BSTNode left;
BSTNode right;
// Constructor
public BSTNode(int value) {
this.data = value;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}2. Key Properties
java
class BSTProperties {
// Property 1: Inorder traversal gives sorted sequence
static void demonstrateInorderProperty() {
BinarySearchTree bst = new BinarySearchTree();
bst.insert(50);
bst.insert(30);
bst.insert(70);
bst.insert(20);
bst.insert(40);
bst.insert(60);
bst.insert(80);
System.out.println("Inorder traversal (sorted):");
bst.inorder(bst.root); // Output: 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
}
// Property 2: For every node, left subtree < node < right subtree
static boolean verifyBSTProperty(BSTNode root, Integer min, Integer max) {
// Base case: empty tree is BST
if (root == null)
return true;
// Check current node's value
if ((min != null && root.data <= min) ||
(max != null && root.data >= max))
return false;
// Recursively check left and right subtrees
return verifyBSTProperty(root.left, min, root.data) &&
verifyBSTProperty(root.right, root.data, max);
}
// Property 3: Minimum is leftmost, Maximum is rightmost
static int findMin(BSTNode root) {
if (root == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Empty tree");
while (root.left != null)
root = root.left;
return root.data;
}
static int findMax(BSTNode root) {
if (root == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Empty tree");
while (root.right != null)
root = root.right;
return root.data;
}
}Basic Operations
Complete BST Implementation
java
class BinarySearchTree {
BSTNode root;
// Constructor
public BinarySearchTree() {
root = null;
}
// ========== SEARCH OPERATION ==========
// Iterative search (more efficient - no recursion overhead)
public boolean searchIterative(int key) {
BSTNode current = root;
while (current != null) {
if (key == current.data)
return true;
else if (key < current.data)
current = current.left;
else
current = current.right;
}
return false;
}
// Recursive search
public boolean search(int key) {
return searchRecursive(root, key);
}
private boolean searchRecursive(BSTNode root, int key) {
// Base case: empty tree or key found
if (root == null)
return false;
if (root.data == key)
return true;
// Recur in appropriate subtree
if (key < root.data)
return searchRecursive(root.left, key);
else
return searchRecursive(root.right, key);
}
// ========== INSERT OPERATION ==========
// Wrapper method for insertion
public void insert(int key) {
root = insertRecursive(root, key);
}
// Recursive insertion
private BSTNode insertRecursive(BSTNode root, int key) {
// Base case: found the position to insert
if (root == null) {
root = new BSTNode(key);
return root;
}
// Recur down the tree
if (key < root.data)
root.left = insertRecursive(root.left, key);
else if (key > root.data)
root.right = insertRecursive(root.right, key);
// If key already exists, do nothing (no duplicates)
return root;
}
// Iterative insertion
public void insertIterative(int key) {
BSTNode newNode = new BSTNode(key);
// If tree is empty
if (root == null) {
root = newNode;
return;
}
BSTNode current = root;
BSTNode parent = null;
// Find the position to insert
while (current != null) {
parent = current;
if (key < current.data)
current = current.left;
else if (key > current.data)
current = current.right;
else
return; // Duplicate key, don't insert
}
// Insert the node
if (key < parent.data)
parent.left = newNode;
else
parent.right = newNode;
}
// ========== DELETE OPERATION ==========
// Wrapper method for deletion
public void delete(int key) {
root = deleteRecursive(root, key);
}
// Recursive deletion
private BSTNode deleteRecursive(BSTNode root, int key) {
// Base case: tree is empty
if (root == null)
return root;
// Recur down the tree to find the node
if (key < root.data)
root.left = deleteRecursive(root.left, key);
else if (key > root.data)
root.right = deleteRecursive(root.right, key);
else {
// Node found! Now delete it
// Case 1: Node has no children (leaf node)
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return null;
// Case 2: Node has one child
if (root.left == null)
return root.right;
else if (root.right == null)
return root.left;
// Case 3: Node has two children
// Get inorder successor (smallest in right subtree)
root.data = findMin(root.right);
// Delete the inorder successor
root.right = deleteRecursive(root.right, root.data);
}
return root;
}
// Helper method to find minimum value
private int findMin(BSTNode root) {
int min = root.data;
while (root.left != null) {
min = root.left.data;
root = root.left;
}
return min;
}
// Alternative: Using inorder predecessor
private int findMax(BSTNode root) {
int max = root.data;
while (root.right != null) {
max = root.right.data;
root = root.right;
}
return max;
}
// ========== TRAVERSAL OPERATIONS ==========
// Inorder: Left -> Root -> Right (gives sorted order)
public void inorder(BSTNode root) {
if (root != null) {
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
inorder(root.right);
}
}
// Preorder: Root -> Left -> Right
public void preorder(BSTNode root) {
if (root != null) {
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
preorder(root.left);
preorder(root.right);
}
}
// Postorder: Left -> Right -> Root
public void postorder(BSTNode root) {
if (root != null) {
postorder(root.left);
postorder(root.right);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
}
}
// Level order (Breadth-First)
public void levelOrder() {
if (root == null)
return;
java.util.Queue<BSTNode> queue = new java.util.LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
BSTNode current = queue.poll();
System.out.print(current.data + " ");
if (current.left != null)
queue.add(current.left);
if (current.right != null)
queue.add(current.right);
}
}
}Demonstration of Basic Operations
java
class BSTBasicDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinarySearchTree bst = new BinarySearchTree();
System.out.println("=== BST OPERATIONS DEMO ===\n");
// ========== INSERTION ==========
System.out.println("1. INSERTION");
System.out.println("Inserting: 50, 30, 70, 20, 40, 60, 80");
bst.insert(50);
bst.insert(30);
bst.insert(70);
bst.insert(20);
bst.insert(40);
bst.insert(60);
bst.insert(80);
System.out.println("\nTree structure:");
System.out.println(" 50");
System.out.println(" / \\");
System.out.println(" 30 70");
System.out.println(" / \\ / \\");
System.out.println(" 20 40 60 80");
// ========== TRAVERSALS ==========
System.out.println("\n2. TRAVERSALS");
System.out.print("Inorder (sorted): ");
bst.inorder(bst.root);
System.out.print("\nPreorder : ");
bst.preorder(bst.root);
System.out.print("\nPostorder : ");
bst.postorder(bst.root);
System.out.print("\nLevel order: ");
bst.levelOrder();
// ========== SEARCH ==========
System.out.println("\n\n3. SEARCH");
int[] searchKeys = {40, 25, 80};
for (int key : searchKeys) {
boolean found = bst.search(key);
System.out.println("Search " + key + ": " + (found ? "Found ✓" : "Not Found ✗"));
}
// ========== DELETION ==========
System.out.println("\n4. DELETION");
// Delete leaf node
System.out.println("\nDeleting 20 (leaf node):");
bst.delete(20);
System.out.print("Inorder: ");
bst.inorder(bst.root);
// Delete node with one child
System.out.println("\n\nDeleting 30 (node with two children):");
bst.delete(30);
System.out.print("Inorder: ");
bst.inorder(bst.root);
// Delete root
System.out.println("\n\nDeleting 50 (root node):");
bst.delete(50);
System.out.print("Inorder: ");
bst.inorder(bst.root);
System.out.println();
}
}
```
**Output:**
```
=== BST OPERATIONS DEMO ===
1. INSERTION
Inserting: 50, 30, 70, 20, 40, 60, 80
Tree structure:
50
/ \
30 70
/ \ / \
20 40 60 80
2. TRAVERSALS
Inorder (sorted): 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Preorder : 50 30 20 40 70 60 80
Postorder : 20 40 30 60 80 70 50
Level order: 50 30 70 20 40 60 80
3. SEARCH
Search 40: Found ✓
Search 25: Not Found ✗
Search 80: Found ✓
4. DELETION
Deleting 20 (leaf node):
Inorder: 30 40 50 60 70 80
Deleting 30 (node with two children):
Inorder: 40 50 60 70 80
Deleting 50 (root node):
Inorder: 40 60 70 80Advanced Operations
1. Find Minimum and Maximum
java
class BSTMinMax {
// Find minimum (leftmost node)
static int findMinimum(BSTNode root) {
if (root == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Tree is empty");
while (root.left != null)
root = root.left;
return root.data;
}
// Find maximum (rightmost node)
static int findMaximum(BSTNode root) {
if (root == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Tree is empty");
while (root.right != null)
root = root.right;
return root.data;
}
// Recursive versions
static int findMinRecursive(BSTNode root) {
if (root == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Tree is empty");
if (root.left == null)
return root.data;
return findMinRecursive(root.left);
}
static int findMaxRecursive(BSTNode root) {
if (root == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Tree is empty");
if (root.right == null)
return root.data;
return findMaxRecursive(root.right);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinarySearchTree bst = new BinarySearchTree();
int[] values = {50, 30, 70, 20, 40, 60, 80};
for (int val : values)
bst.insert(val);
System.out.println("Minimum value: " + findMinimum(bst.root));
System.out.println("Maximum value: " + findMaximum(bst.root));
}
}2. Find Inorder Successor and Predecessor
java
class BSTSuccessorPredecessor {
// Find inorder successor (next larger element)
static BSTNode findInorderSuccessor(BSTNode root, int key) {
BSTNode successor = null;
BSTNode current = root;
while (current != null) {
if (key < current.data) {
successor = current;
current = current.left;
} else if (key > current.data) {
current = current.right;
} else {
// Key found
if (current.right != null) {
// If right subtree exists, successor is minimum in right subtree
successor = current.right;
while (successor.left != null)
successor = successor.left;
}
break;
}
}
return successor;
}
// Find inorder predecessor (next smaller element)
static BSTNode findInorderPredecessor(BSTNode root, int key) {
BSTNode predecessor = null;
BSTNode current = root;
while (current != null) {
if (key > current.data) {
predecessor = current;
current = current.right;
} else if (key < current.data) {
current = current.left;
} else {
// Key found
if (current.left != null) {
// If left subtree exists, predecessor is maximum in left subtree
predecessor = current.left;
while (predecessor.right != null)
predecessor = predecessor.right;
}
break;
}
}
return predecessor;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinarySearchTree bst = new BinarySearchTree();
int[] values = {50, 30, 70, 20, 40, 60, 80};
for (int val : values)
bst.insert(val);
System.out.println("Tree (Inorder): 20 30 40 50 60 70 80");
int key = 50;
BSTNode successor = findInorderSuccessor(bst.root, key);
BSTNode predecessor = findInorderPredecessor(bst.root, key);
System.out.println("\nFor key " + key + ":");
System.out.println("Successor: " + (successor != null ? successor.data : "null"));
System.out.println("Predecessor: " + (predecessor != null ? predecessor.data : "null"));
}
}3. Lowest Common Ancestor (LCA)
java
class BSTLowestCommonAncestor {
// Find LCA in BST (efficient approach using BST property)
static BSTNode findLCA(BSTNode root, int n1, int n2) {
if (root == null)
return null;
// If both n1 and n2 are smaller, LCA is in left subtree
if (root.data > n1 && root.data > n2)
return findLCA(root.left, n1, n2);
// If both n1 and n2 are greater, LCA is in right subtree
if (root.data < n1 && root.data < n2)
return findLCA(root.right, n1, n2);
// If one is on left and other is on right, or one equals root, then root is LCA
return root;
}
// Iterative approach
static BSTNode findLCAIterative(BSTNode root, int n1, int n2) {
while (root != null) {
if (root.data > n1 && root.data > n2)
root = root.left;
else if (root.data < n1 && root.data < n2)
root = root.right;
else
break;
}
return root;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinarySearchTree bst = new BinarySearchTree();
int[] values = {50, 30, 70, 20, 40, 60, 80, 10, 25, 35, 45};
for (int val : values)
bst.insert(val);
System.out.println("Tree structure:");
System.out.println(" 50");
System.out.println(" / \\");
System.out.println(" 30 70");
System.out.println(" / \\ / \\");
System.out.println(" 20 40 60 80");
System.out.println(" / \\ / \\");
System.out.println(" 10 25 35 45");
int[][] pairs = {{10, 25}, {20, 40}, {10, 45}, {35, 45}};
System.out.println("\nLowest Common Ancestors:");
for (int[] pair : pairs) {
BSTNode lca = findLCA(bst.root, pair[0], pair[1]);
System.out.println("LCA(" + pair[0] + ", " + pair[1] + ") = " +
(lca != null ? lca.data : "null"));
}
}
}4. Check if Binary Tree is BST
java
class ValidateBST {
// Method 1: Using Min-Max range
static boolean isBST(BSTNode root) {
return isBSTUtil(root, Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
static boolean isBSTUtil(BSTNode node, int min, int max) {
// Empty tree is BST
if (node == null)
return true;
// Check if current node violates BST property
if (node.data <= min || node.data >= max)
return false;
// Check recursively for left and right subtrees
return isBSTUtil(node.left, min, node.data) &&
isBSTUtil(node.right, node.data, max);
}
// Method 2: Using Inorder traversal (should be sorted)
static Integer prev = null;
static boolean isBSTInorder(BSTNode root) {
if (root == null)
return true;
// Check left subtree
if (!isBSTInorder(root.left))
return false;
// Check current node
if (prev != null && root.data <= prev)
return false;
prev = root.data;
// Check right subtree
return isBSTInorder(root.right);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Valid BST
BSTNode validRoot = new BSTNode(50);
validRoot.left = new BSTNode(30);
validRoot.right = new BSTNode(70);
validRoot.left.left = new BSTNode(20);
validRoot.left.right = new BSTNode(40);
System.out.println("Valid BST check: " + isBST(validRoot));
// Invalid BST
BSTNode invalidRoot = new BSTNode(50);
invalidRoot.left = new BSTNode(30);
invalidRoot.right = new BSTNode(70);
invalidRoot.left.left = new BSTNode(20);
invalidRoot.left.right = new BSTNode(65); // Invalid! 65 > 50
System.out.println("Invalid BST check: " + isBST(invalidRoot));
}
}5. Kth Smallest/Largest Element
java
class BSTKthElement {
static int count;
static int result;
// Find kth smallest element (using inorder traversal)
static int kthSmallest(BSTNode root, int k) {
count = 0;
result = -1;
kthSmallestUtil(root, k);
return result;
}
static void kthSmallestUtil(BSTNode root, int k) {
if (root == null)
return;
// Inorder: left -> root -> right
kthSmallestUtil(root.left, k);
count++;
if (count == k) {
result = root.data;
return;
}
kthSmallestUtil(root.right, k);
}
// Find kth largest element (reverse inorder)
static int kthLargest(BSTNode root, int k) {
count = 0;
result = -1;
kthLargestUtil(root, k);
return result;
}
static void kthLargestUtil(BSTNode root, int k) {
if (root == null)
return;
// Reverse inorder: right -> root -> left
kthLargestUtil(root.right, k);
count++;
if (count == k) {
result = root.data;
return;
}
kthLargestUtil(root.left, k);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinarySearchTree bst = new BinarySearchTree();
int[] values = {50, 30, 70, 20, 40, 60, 80};
for (int val : values)
bst.insert(val);
System.out.println("Inorder: 20 30 40 50 60 70 80");
for (int k = 1; k <= 7; k++) {
System.out.println(k + "th smallest: " + kthSmallest(bst.root, k));
}
System.out.println();
for (int k = 1; k <= 7; k++) {
System.out.println(k + "th largest: " + kthLargest(bst.root, k));
}
}
}