Introduction to Trees
A tree is a hierarchical data structure that consists of nodes connected by edges. Unlike linear data structures (arrays, linked lists), trees represent hierarchical relationships and are one of the most important non-linear data structures in computer science.
Why Trees?
Imagine organizing your computer’s file system, representing an organization’s hierarchy, or managing a database index. All these scenarios naturally form tree-like structures where:
- There’s a starting point (root)
- Elements have parent-child relationships
- No cycles exist
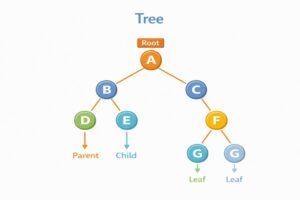
Tree Terminology
Before diving deep, let’s understand the key terms:
- Root: The topmost node (starting point)
- Parent: A node that has child nodes below it
- Child: A node that has a parent above it
- Leaf: A node with no children (end points)
- Siblings: Nodes that share the same parent
- Height: Length of the longest path from a node to a leaf
- Depth: Length of the path from root to that node
- Subtree: A tree formed by a node and all its descendants
Visual Example:
A ← Root (Height: 3, Depth: 0)
/ \
B C ← Level 1 (B and C are siblings)
/ \ \
D E F ← Level 2 (Leaves)
/
G ← Level 3 (Leaf, Height: 0, Depth: 3)