Because Strings are immutable, simple operations can be costly if done incorrectly. Here is how to handle them.
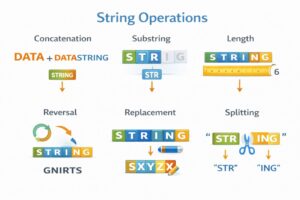
Common Operations:
- Concatenation: Joining two strings together.
- Substring: Extracting a portion of a string.
- Length: Counting the number of characters.
- Searching: Finding the index of a specific character or pattern.
Java Implementation: String Methods
public class StringBasics {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. Creation
String str1 = "Hello"; // String Literal (Stored in Pool)
String str2 = new String("World"); // String Object (Stored in Heap)
// 2. Concatenation
String result = str1 + " " + str2;
System.out.println(result); // Output: Hello World
// 3. Length (O(1))
System.out.println("Length: " + result.length()); // Output: 11
// 4. CharAt (Accessing character at index - O(1))
System.out.println("Char at index 1: " + str1.charAt(1)); // Output: e
// 5. Substring (Extracting part - O(n))
// substring(start, end) -> includes start, excludes end
System.out.println("Substring: " + result.substring(0, 5)); // Output: Hello
// 6. Equality Check (Critical in Java!)
// ALWAYS use .equals(), NEVER use == for strings
System.out.println(str1.equals("Hello")); // true
}
}
