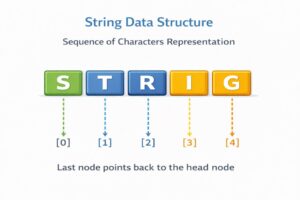
A String is effectively a sequence of characters. In computer science, it is one of the most widely used data structures because almost all data communication involves text (names, addresses, messages, URLs).
Under the Hood: The “Array” Connection
Technically, a String is implemented as an array of characters.
- If you have a string “HELLO”, it is stored in memory like a character array: [‘H’, ‘E’, ‘L’, ‘L’, ‘O’].
- However, in languages like Java, Strings are treated as Objects, giving them powerful built-in methods.
Key Characteristic: Immutability
In Java, Strings are Immutable. This means once a String object is created, it cannot be changed.
- If you try to modify it (e.g., str = str + ” World”), Java doesn’t actually change the original string. instead, it creates a brand new string in memory and discards the old one.
- Why? This makes Strings safe to use in multi-threaded environments and saves memory via the “String Pool”.
Real-Life Analogy
The Printed Book: Think of a String like a page in a printed book. You cannot erase or change a word on that page once it is printed. If you want to change the story, you have to print a whole new page (create a new String object). You cannot just modify the ink on the existing paper.
Famous String Algorithms (DSA Topics)
To master DSA, you need to solve specific problems related to strings.
A. Palindrome Check
A string is a palindrome if it reads the same forward and backward (e.g., “MADAM”).
- Logic: Use two pointers (Start and End). Compare characters and move inwards.
B. Anagram Check
Two strings are anagrams if they contain the same characters in different orders (e.g., “LISTEN” and “SILENT”).
- Logic: Sort both strings and compare (O(N log N)) OR use a frequency array (O(N)).
Java Code: Palindrome Check (Two Pointers)
public class PalindromeCheck {
public static boolean isPalindrome(String str) {
int left = 0;
int right = str.length() - 1;
while (left < right) {
// Compare characters
if (str.charAt(left) != str.charAt(right)) {
return false; // Mismatch found
}
left++;
right--;
}
return true; // Reached middle without mismatch
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input = "racecar";
System.out.println(input + " is palindrome? " + isPalindrome(input));
}
}
