Arrays are categorized based on the number of indices used to access elements.
A. One-Dimensional Array (1D)
A One-Dimensional Array (or 1D Array) is the simplest form of an array. It is a linear list of elements of the same type, stored in contiguous memory locations. You can imagine it as a single row of lockers, where each locker has a unique index number. 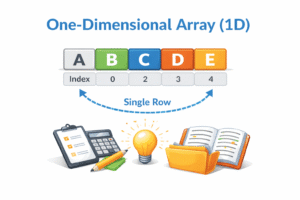 Java Implementation
Java Implementation
public class OneDimensionalArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. Static Initialization (Declaration + Creation + Assignment)
// Used when we already know the data
int[] marks = {85, 90, 78, 92, 88};
System.out.println("First student's mark: " + marks[0]); // Accessing index 0
// 2. Dynamic Initialization (Declaration + Memory Allocation)
// Used when we don't know the values yet
String[] fruits = new String[4]; // Creates an empty array of size 4
// Assigning values manually
fruits[0] = "Apple";
fruits[1] = "Banana";
fruits[2] = "Mango";
fruits[3] = "Orange";
System.out.println("\nList of Fruits:");
// Traversal using a for-loop
for (int i = 0; i < fruits.length; i++) {
System.out.println("Index " + i + ": " + fruits[i]);
}
// Traversal using Enhanced For-Loop (For-Each)
System.out.println("\nMarks:");
for (int m : marks) {
System.out.print(m + " ");
}
}
}
- Analogy: A row of lockers in a school hallway.
- Use Case: Storing a list of student marks or daily temperatures.
B. Multi-Dimensional Array (2D, 3D)
Arrays within arrays. The most common is the 2D Array (Matrix).
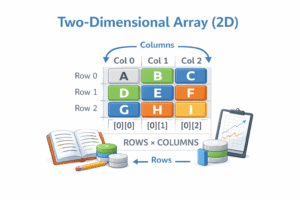
Java Implementation
public class TwoDimensionalArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declaration: int[rows][columns]
// Example: A 3x3 Matrix
int[][] matrix = {
{1, 2, 3}, // Row 0
{4, 5, 6}, // Row 1
{7, 8, 9} // Row 2
};
System.out.println("Element at Row 1, Column 2 (Index 1,2): " + matrix[1][2]); // Output: 6
System.out.println("\nDisplaying the 3x3 Matrix:");
// Outer loop for Rows
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
// Inner loop for Columns
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println(); // New line after every row
}
}
}
- Analogy: A spreadsheet or a chessboard (Rows and Columns).
- Use Case: Storing an image (pixels), matrices, or tables.
