Array Data Structure
An Array is a fundamental linear data structure that stores a collection of elements of the same data type in a contiguous block of memory.
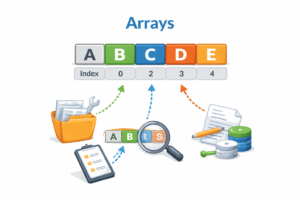
- Contiguous Memory: Elements are stored side-by-side in memory, leaving no gaps.
- Indexing: Each element is identified by an index or position, starting from 0.
- Fixed Size: Once an array is created, its size cannot be changed. To add more elements beyond its capacity, you must create a new, larger array.
Why use Arrays?
Arrays are the building blocks for more complex data structures like Heaps, Hash Tables, and Vectors. Their biggest advantage is speed:
- Fast Access: You can access any element instantly (O(1)) if you know its index.
- Cache Friendliness: Because data is stored together in memory, modern CPUs can process arrays very efficiently.
Common Array Operations
Here are the standard operations you can perform on an array.
- Traversal: Visiting every element (e.g., to print them).
- Insertion: Adding an element at a specific position.
- Deletion: Removing an element from a specific position.
- Searching: Finding the index of a specific element.
- Updating: Changing the value at a specific index.
Time Complexity Table
|
Operation |
Time Complexity |
Explanation |
|
Access |
$O(1)$ |
Instant access using index. |
|
Search |
$O(n)$ |
In worst case (Linear Search), you might check every element. |
|
Insertion |
$O(n)$ |
You may need to shift all subsequent elements. |
|
Deletion |
$O(n)$ |
You may need to shift elements to fill the gap. |
Real-World Applications of Arrays
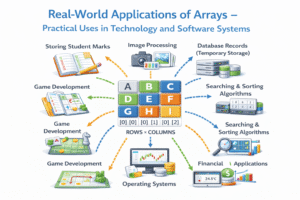
Arrays are widely used in computer programming:
- Image Processing: Images are stored as 2D arrays of pixels (or 3D for RGB colors).
- Databases: Tables in a database are often implemented using 2D arrays.
- Mathematical Computing: Matrices are essential for solving linear equations in engineering.
- Sorting Algorithms: Algorithms like Merge Sort, Quick Sort, and Heap Sort operate on arrays.
- Lookup Tables: Used to store pre-calculated values for optimization (Dynamic Programming).
- Audio Processing: Arrays represent audio signals, where elements correspond to signal
