A Queue is a linear data structure that follows the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle. The first element added to the queue is the first one to be removed. 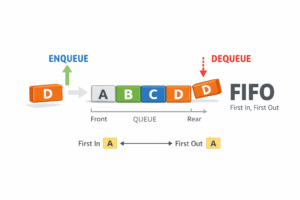
Real-World Analogy
Imagine a line of people waiting at a movie ticket counter. The person who arrives first gets served first, and new people join at the end of the line (Rear). Core Operations
- Enqueue: Add an element to the rear of the queue.
- Dequeue: Remove and return the front element.
- Front/Peek: View the front element without removing it.
- Rear: View the last element.
Java Implementation (Array-Based)
Below is the Java code for a simple Queue .
class Queue {
private int maxSize;
private int[] queueArray;
private int front;
private int rear;
private int currentSize;
public Queue(int size) {
this.maxSize = size;
this.queueArray = new int[maxSize];
this.front = 0;
this.rear = -1;
this.currentSize = 0;
}
// Enqueue: Add to rear
public void enqueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("Queue is full! Cannot enqueue " + value);
return;
}
rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize; // Handles wrapping for array
queueArray[rear] = value;
currentSize++;
System.out.println("Enqueued: " + value);
}
// Dequeue: Remove from front
public int dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty! Cannot dequeue");
return -1;
}
int value = queueArray[front];
front = (front + 1) % maxSize;
currentSize--;
System.out.println("Dequeued: " + value);
return value;
}
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty!");
return -1;
}
return queueArray[front];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return currentSize == 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return currentSize == maxSize;
}
}
