A Stack is a linear data structure that operates on the LIFO (Last In, First Out) principle. This means the last element added to the stack is the first one to be removed. 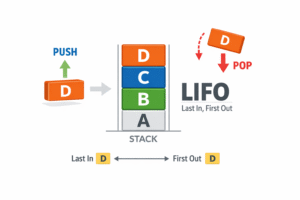
Real-World Analogy
Think of a stack of plates in a cafeteria. You add new plates on top (push) and remove plates from the top (pop). You cannot remove a plate from the middle or bottom without first removing the ones on top.
Key Characteristics
- LIFO Principle: The last item entered is the first item accessed.
- Restricted Access: You can only add or remove elements from one end, known as the “Top”.
Core Operations
- Push: Add an element to the top of the stack.
- Pop: Remove and return the top element.
- Peek/Top: View the top element without removing it.
- isEmpty: Check if the stack is empty.
- Size: Get the count of elements in the stack.
Java Implementation (Array-Based)
Here is a robust implementation of a Stack using an array in Java .
class Stack {
private int maxSize;
private int[] stackArray;
private int top;
// Constructor to initialize stack
public Stack(int size) {
this.maxSize = size;
this.stackArray = new int[maxSize];
this.top = -1; // Indicates empty stack
}
// Push operation: Add element to top
public void push(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("Stack Overflow! Cannot push " + value);
return;
}
stackArray[++top] = value;
System.out.println("Pushed: " + value);
}
// Pop operation: Remove element from top
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Stack Underflow! Stack is empty");
return -1;
}
int value = stackArray[top--];
System.out.println("Popped: " + value);
return value;
}
// Peek operation: View top element
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty");
return -1;
}
return stackArray[top];
}
// Helper methods
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (top == -1);
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (top == maxSize - 1);
}
}
