A real-world stack allows operations at one end only. For example, we can place or remove a card or plate from the top of the stack only. At any given time, we can only access the top element of a stack.
This feature makes it LIFO data structure. LIFO stands for Last-in-first-out. Here, the element which is placed (inserted or added) last, is accessed first. In stack terminology, insertion operation is called PUSH operation and removal operation is called POP operation.
Reference Videos: Stack
Stack Representation
The following diagram depicts a stack and its operations
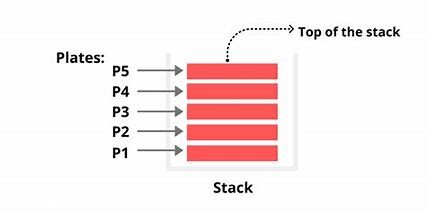
A stack can be implemented by means of Array, Structure, Pointer, and Linked List. Stack can either be a fixed size one or it may have a sense of dynamic resizing. Here, we are going to implement stack using arrays, which makes it a fixed size stack implementation.
Basic Operations
Stack operations may involve initializing the stack, using it and then de-initializing it. Apart from these basic stuffs, a stack is used for the following two primary operations −
- push() − Pushing (storing) an element on the stack.
- pop() − Removing (accessing) an element from the stack. When data is PUSHed onto stack.
To use a stack efficiently, we need to check the status of stack as well. For the same purpose, the following functionality is added to stacks −
- peek() − get the top data element of the stack, without removing it.
- isFull() − check if stack is full.
- isEmpty() − check if stack is empty.
At all times, we maintain a pointer to the last Pushed data on the stack. The top pointer provides top value of the stack without actually removing it.
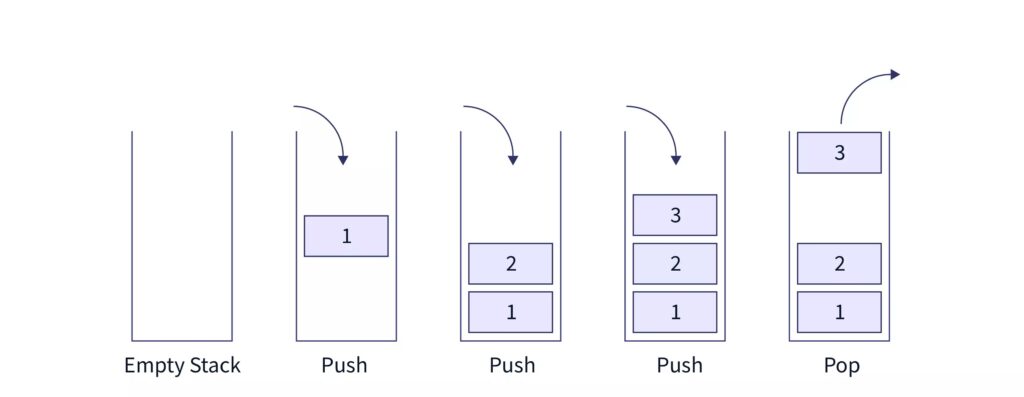
At all times, we maintain a pointer to the last PUSHed data on the stack. The top pointer provides top value of the stack without actually removing it.
First we should learn about procedures to support stack functions −
peek ()
Algorithm of peek () function −
begin procedure peek return stack[top]
end procedure
isfull()
Algorithm of isfull() function −
begin procedure isfull
if top equals to MAXSIZE return true
else
return false endif
end procedure
isempty()
Algorithm of isempty() function −
begin procedure isempty
if top less than 1 return true
else
return false endif
end procedure
Implementation of isempty() function in C programming language is slightly different. We initialize top at -1, as the index in array starts from 0. So we check if the top is below zero or -1 to determine if the stack is empty. Here’s the code −
Push Operation
The process of putting a new data element onto stack is known as a Push Operation. Push operation involves a series of steps −
- Step 1 − Checks if the stack is full.
- Step 2 − If the stack is full, produces an error and exit.
- Step 3 − If the stack is not full, increments top to point next empty space.
- Step 4 − Adds data element to the stack location, where top is pointing.
- Step 5 − Returns success.
Pop Operation
Accessing the content while removing it from the stack, is known as a Pop Operation. In an array implementation of pop() operation, the data element is not actually removed, instead the top is decremented to a lower position in the stack to point to the next value. But in linked-list implementation, pop() actually removes data elements and deallocates memory space.
A Pop operation may involve the following steps −
- Step 1 − Check if the stack is empty.
- Step 2 − If the stack is empty, produce an error and exit.
- Step 3 − If the stack is not empty, access the data element at which top is pointing.
- Step 4 − Decreases the value of top by 1.
- Step 5 − Returns success.
