A linked list is a sequence of data structures, which are connected together via links. Linked List is a sequence of links which contains items. Each link contains a connection to another link. Linked list is the second most-used data structure after array. Following are the important terms to understand the concept of Linked List.
Reference Video: Linked List
- Link − Each link of a linked list can store a data called an element.
- Next − Each link of a linked list contains a link to the next link called Next.
- LinkedList − A Linked List contains the connection link to the first link called First.
Linked List Representation:
Linked list can be visualized as a chain of nodes, where every node points to the next node.

As per the above illustration, following are the important points to be considered.
- Linked List contains a link element called first.
- Each link carries a data field(s) and a link field called next.
- Each link is linked with its next link using its next link.
- Last link carries a link as null to mark the end of the list.
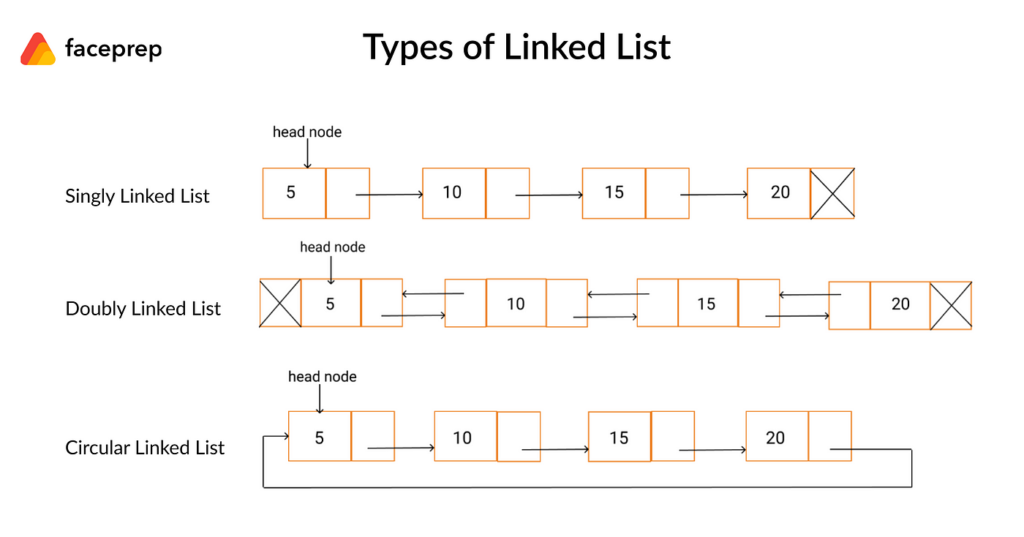
Types of Linked List:
Following are the various types of linked list.
- Simple Linked List − Item navigation is forward only.
- Doubly Linked List − Items can be navigated forward and backward.
- Circular Linked List − Last item contains link of the first element as next and the first element has a link to the last element as previous.
Basic Operations
Following are the basic operations supported by a linked list.
- Insertion − Adds an element at the beginning of the linked list.
- Deletion − Deletes an element at the beginning of the linked list.
- Display − Displays the complete linked list.
- Search − Searches an element using the given key.
- Delete − Deletes an element using the given key.
Insertion Operation
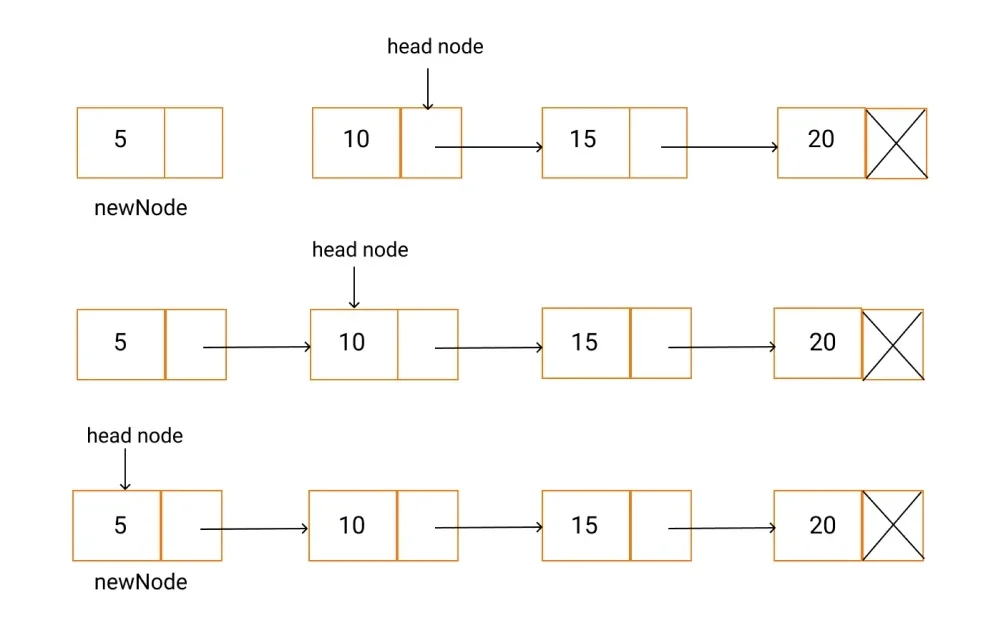
Adding a new node in linked list is a more than one step activity. We shall learn this with diagrams here. First, create a node using the same structure and find the location where it has to be inserted.