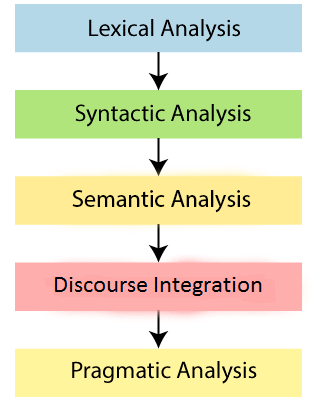
1. Lexical and Morphological Analysis
Lexical Analysis
Lexical analysis deals with identifying words (lexemes) and converting text into smaller meaningful units called tokens.
Main tasks:
- Tokenization: Breaking text into tokens.
- Example: “I love programming” → [“I”, “love”, “programming”].
- Part-of-Speech (POS) Tagging: Assigning grammatical roles (noun, verb, adjective, etc.) to each token.
- Example: “I am reading a book” →
- “I” → Pronoun (PRP)
- “am” → Verb (VBP)
- “reading” → Verb (VBG)
- “a” → Article (DT)
- “book” → Noun (NN)
- Example: “I am reading a book” →
Importance:
- Helps in word identification for further processing.
- Simplifies text for downstream tasks through tokenization and stemming, improving accuracy.
Morphological Analysis
This focuses on morphemes, the smallest units of meaning in language. Morphemes can be:
- Free morphemes (independent words like “cat”)
- Bound morphemes (prefixes/suffixes like “un-” or “-ing”)
Main tasks:
- Stemming: Reducing words to their root form. (running → run)
- Lemmatization: Converting words to their dictionary form, considering context. (better → good)
Importance:
- Provides insights into word structure.
- Improves accuracy in POS tagging, parsing, and machine translation.
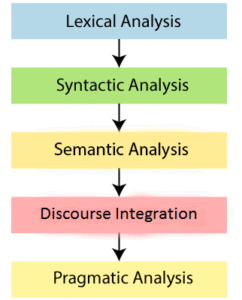
2. Syntactic Analysis (Parsing)
Syntactic analysis checks how words are arranged according to grammar rules. It builds a parse tree showing the structure of a sentence and how subjects, verbs, and objects relate.
Key aspects:
- POS Tagging: Identifying grammatical categories of words.
- Ambiguity Resolution: Handling words with multiple meanings (e.g., “book” as a noun or verb).
Examples:
- Correct syntax: “John eats an apple.”
- Incorrect syntax: “Apple eats John an.”
Importance:
- Ensures sentences follow grammatical rules.
- Supports NLP applications like machine translation, sentiment analysis, and information retrieval by clarifying sentence structure.
3. Semantic Analysis
Semantic analysis focuses on the meaning of words and sentences, ensuring that text is contextually relevant and logically coherent.
Key tasks:
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): Identifies entities such as people, places, dates, or organizations.
- Example: “Tesla announced its new electric vehicle in California” →
- “Tesla” → Organization
- “California” → Location
- Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD): Determines the correct meaning of a word based on context.
- Example: “bank” → financial institution vs. riverbank.
- Example: “Tesla announced its new electric vehicle in California” →
Example:
- “Apple eats a John.” → Grammatically correct, but semantically illogical.
Importance:
- Ensures language is meaningful in context.
- Used in machine translation, question answering, and information retrieval.
4. Discourse Integration
Discourse integration ensures consistency and coherence across multiple sentences or paragraphs. It connects individual sentences to form a meaningful whole.
Key aspects:
- Anaphora Resolution: Identifying references to earlier entities.
- Example: “Taylor went to the store. She bought groceries.” → “She” refers to Taylor.
- Contextual References: Understanding meaning based on context.
- Example: “It was a great day.” → The meaning depends on the event being described.
Examples:
- “Taylor went to the store to buy groceries. She realized she forgot her wallet.” → “She” refers back to Taylor.
- “This is unfair!” → Requires previous context to understand what “this” means.
Importance:
- Maintains coherence in longer texts.
- Essential in chatbots, summarization, and machine translation.
5. Pragmatic Analysis
Pragmatic analysis looks beyond literal meaning and considers intent, tone, and context to interpret communication.
Key tasks:
- Understanding Intentions: Recognizing implied meaning.
- Example: “Can you pass the salt?” → A polite request, not a question about ability.
- Figurative Language: Understanding idioms, metaphors, and non-literal phrases.
- Example: “I’m falling for you.” → Means “I love you,” not physically falling.
Examples:
- “Hello! What time is it?” → Could mean just asking for time or worrying about being late.
- “I’m falling for you.” → Figurative expression of affection.
Importance:
- Helps machines grasp speaker intent, sarcasm, and emotions
- Used in sentiment analysis, conversational AI, and chatbots for natural interactions.
