Java – Arrays
Java provides a data structure, the array, which stores a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type. An array is used to store a collection of data, but it is often more useful to think of an array as a collection of variables of the same type.
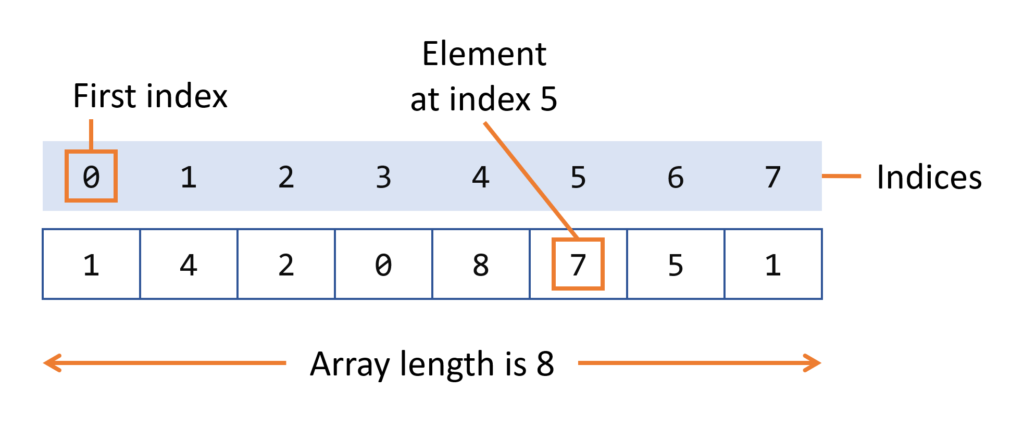
Instead of declaring individual variables, such as number0, number1, …, and number99, you declare one array variable such as numbers and use numbers[0], numbers[1], and …, numbers[99] to represent individual variables.
This tutorial introduces how to declare array variables, create arrays, and process arrays using indexed variables.
Video on Arrays in Java
Declaring Array Variables
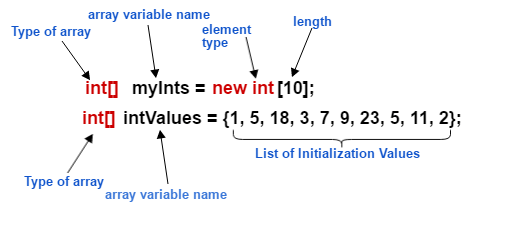
To use an array in a program, you must declare a variable to reference the array, and you must specify the type of array the variable can reference. Here is the syntax for declaring an array variable −
Syntax:
dataType[] arrayRefVar; // preferred way.
or
dataType arrayRefVar[]; // works but not preferred way.
Note − The style dataType[] arrayRefVar is preferred. The style dataType arrayRefVar[] comes from the C/C++ language and was adopted in Java to accommodate C/C++ programmers.
The following code snippets are examples of this syntax −
double[] myList; // preferred way.
or
double myList[]; // works but not preferred way.Creating Arrays
Syntax:
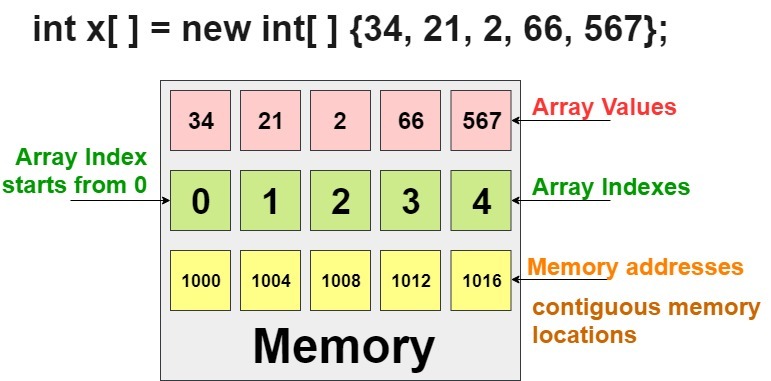
arrayRefVar = new dataType[arraySize];The above statement does two things −
- It creates an array using new dataType[arraySize].
- It assigns the reference of the newly created array to the variable arrayRefVar.
Know More Visit this Blog on Arrays programms
Declaring an array variable, creating an array, and assigning the reference of the array to the variable can be combined in one statement, as shown below −
dataType[] arrayRefVar = new dataType[arraySize];Alternatively you can create arrays as follows −
dataType[] arrayRefVar = {value0, value1, ..., valuek};The array elements are accessed through the index. Array indices are 0-based; that is, they start from 0 to arrayRefVar.length-1.
Example
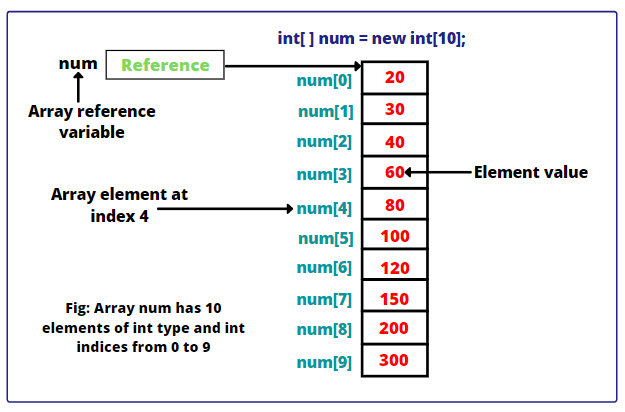
Following statement declares an array variable, myList, creates an array of 10 elements of double type and assigns its reference to myList −
double[] myList = new double[10];Following picture represents array num. Here, num holds ten integer values and the indices are from 0 to 9.
Example
Here is a complete example showing how to create, initialize, and process arrays.
public class TestArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] myList = {1.9, 2.9, 3.4, 3.5};
// Print all the array elements
for (int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++) {
System.out.println(myList[i] + " ");
}
// Summing all elements
double total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++) {
total += myList[i];
}
System.out.println("Total is " + total);
// Finding the largest element
double max = myList[0];
for (int i = 1; i < myList.length; i++) {
if (myList[i] > max) max = myList[i];
}
System.out.println("Max is " + max);
}
}
Output:
1.9
2.9
3.4
3.5
Total is 11.7
Max is 3.5Arrays Programms
The foreach Loops
JDK 1.5 introduced a new for loop known as foreach loop or enhanced for loop, which enables you to traverse the complete array sequentially without using an index variable.
Example
public class TestArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] myList = {1.9, 2.9, 3.4, 3.5};
// Print all the array elements
for (double element: myList) {
System.out.println(element);
}
}
}Output:
1.9
2.9
3.4
3.5Multi-Dimensional Array
A multi-dimensional array is very much similar to a single dimensional array. It can have multiple rows and multiple columns unlike single dimensional array, which can have only one full row or one full column.
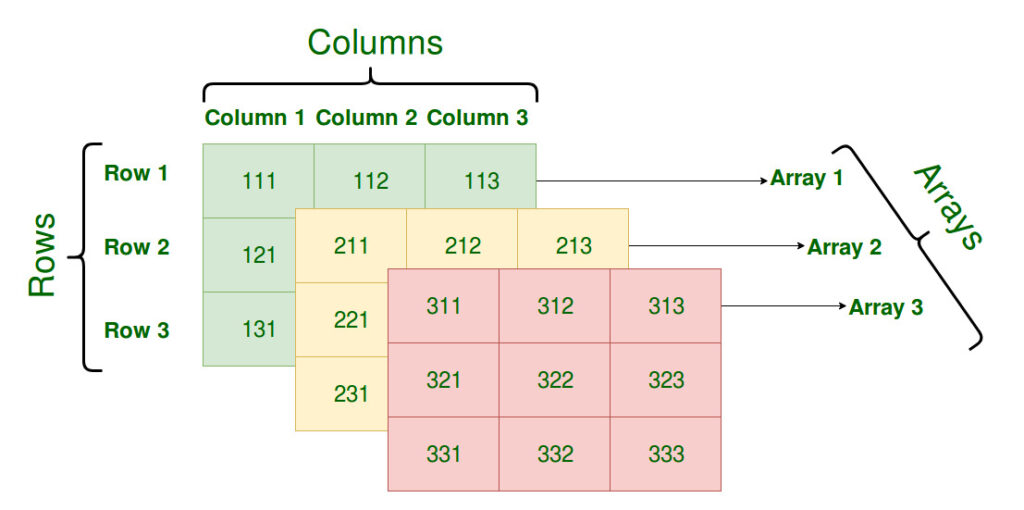
Array Declaration
Syntax:
datatype[ ][ ] identifier;
or
datatype identifier[ ][ ];Initialization of Array
new operator is used to initialize an array.
Example:
int[ ][ ] arr = new int[10][10]; //10 by 10 is the size of array.
or
int[ ][ ] arr = {{1,2,3,4,5},{6,7,8,9,10},{11,12,13,14,15}};
// 3 by 5 is the size of the array.Accessing array element
For both, row and column, the index begins from 0.
Syntax:
array_name[m-1][n-1]Example
int arr[ ][ ] = {{1,2,3,4,5},{6,7,8,9,10},{11,12,13,14,15}};
System.out.println("Element at (2,3) place" + arr[1][2]);Jagged Array
Jagged means to have an uneven edge or surface. In java, a jagged array means to have a multi-dimensional array with uneven size of rows in it.
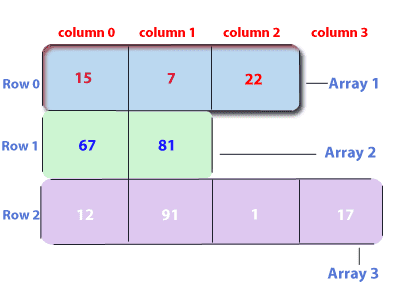
Initialization of Jagged Array
new operator is used to initialize an array.
Example:
int[ ][ ] arr = new int[3][ ]; //there will be 10 arrays whose size is variable
arr[0] = new int[3];
arr[1] = new int[4];
arr[2] = new int[5];The Arrays Class
The java.util.Arrays class contains various static methods for sorting and searching arrays, comparing arrays, and filling array elements. These methods are overloaded for all primitive types.
| Sr.No. | Method & Description |
| 1 | public static int binarySearch(Object[] a, Object key) Searches the specified array of Object ( Byte, Int , double, etc.) for the specified value using the binary search algorithm. The array must be sorted prior to making this call. This returns index of the search key, if it is contained in the list; otherwise, it returns ( – (insertion point + 1)). |
| 2 | public static boolean equals(long[] a, long[] a2) Returns true if the two specified arrays of longs are equal to one another. Two arrays are considered equal if both arrays contain the same number of elements, and all corresponding pairs of elements in the two arrays are equal. This returns true if the two arrays are equal. Same method could be used by all other primitive data types (Byte, short, Int, etc.) |
| 3 | public static void fill(int[] a, int val) Assigns the specified int value to each element of the specified array of ints. The same method could be used by all other primitive data types (Byte, short, Int, etc.) |
| 4 | public static void sort(Object[] a) Sorts the specified array of objects into an ascending order, according to the natural ordering of its elements. The same method could be used by all other primitive data types ( Byte, short, Int, etc.) |
Recommended Articles
- Basics of Java
- Features of Java
- Control Statements in Java
- Loop Statements in Java
- Array Handling in Java
- OOP’s Concept in Java
- Java Networking
- Exception Handling in Java
