Quick Sort Algorithm
Quicksort is an efficient sorting algorithm that follows the divide and conquer strategy. It works by selecting a pivot element and partitioning the array so that all elements smaller than the pivot come before it, and all elements greater come after. This process is repeated for the left and right subarrays until the entire list is sorted.
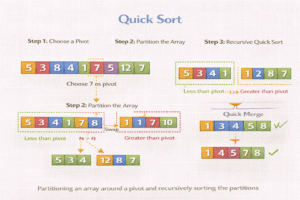
Working of Quick sort
- Pick a Pivot: Choose one number from the list. This is called the pivot.
- Divide the List: Rearrange the list so that:
- All numbers smaller than the pivot go to its left.
- All numbers greater than the pivot go to its right.
- Repeat:
- Now take the left and right sides (subarrays) and do the same steps again—choose a pivot, divide into smaller and greater parts.
- Keep Splitting until each part has only one number.
- Once everything is divided like this, the list becomes automatically sorted!
Quicksort Java code:
public class QuickSort {
// Function to perform Quick Sort
public static void quickSort(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
// Partition index
int pi = partition(arr, low, high);
// Sort elements before and after partition
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1);
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high);
}
}
// Partition function
public static int partition(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
int pivot = arr[high]; // Choosing last element as pivot
int i = low - 1;
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
// If current element is smaller than pivot
if (arr[j] < pivot) {
i++;
// Swap arr[i] and arr[j]
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
// Place pivot at correct position
int temp = arr[i + 1];
arr[i + 1] = arr[high];
arr[high] = temp;
return i + 1;
}
// Function to print array
public static void printArray(int[] arr) {
for (int num : arr) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5};
System.out.println("Before Sorting:");
printArray(arr);
quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
System.out.println("After Sorting:");
printArray(arr);
}
}
Time Complexity
| Case | Time Complexity | Explanation |
| Best Case | O (n log n) | When the pivot always splits the array into two equal halves. |
| Average Case | O (n log n) | On average, Quicksort performs well with balanced partitions. |
| Worst Case | O(n²) | Happens when the pivot is always the smallest or largest element (e.g., sorted array with bad pivot choice). |
