Linear Search Agorithm
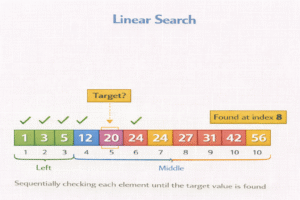
Linear Search (also called sequential search) is a simple searching algorithm that checks each element in a list one by one until it finds the target element or reaches the end of the list.
It works on both sorted and unsorted arrays.
How Linear Search Works (Step-by-Step)
- Start from the first element of the array.
- Compare each element with the target/key you are looking for.
- If a match is found, return the index.
- If no match is found by the end, return -1 (or say “not found”).
Example
Array: [12, 45, 67, 23, 89]
Target: 23
Step-by-Step Execution:
| Step | Element Checked | Is it equal to 23? | Result |
| 1 | 12 | No | Continue |
| 2 | 45 | No | Continue |
| 3 | 67 | No | Continue |
| 4 | 23 | Yes | Found at index 3 |
Linear Search python code:
function linearSearch (arr, target): for i = 0 to len(arr) - 1: if arr[i] == target: return i return -1
Time Complexity
| Case | Time Complexity |
| Best Case | O(1) |
| Average | O(n) |
| Worst Case | O(n) |
- n = number of elements
Space Complexity
- O (1) — no extra space used
Key Features:
- Simple and easy
- Works for unsorted arrays
- Not efficient for large data sets
