Binary Search Algorithm
Binary Search is a fast and efficient searching algorithm that works only on sorted arrays or lists. It follows the divide and conquer strategy to reduce the search space by half in each step. In Binary Search:
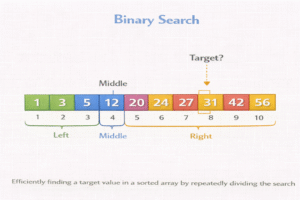
- The search begins by comparing the target value with the middle element of the array.
- If the target matches the middle element, the search is successful.
- If the target is less than the middle element, the search continues in the left half of the array.
- If the target is greater than the middle element, the search continues in the right half.
- This process repeats until the element is found or the subarray size becomes zero (i.e., the element is not found).
Example of Binary Search
Input (Sorted Array): [5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40] Target Element: 25 Step-by-Step Search Process: Initialize: low = 0 (first index) high = 7 (last index) mid = (0 + 7) / 2 = 3 → array [3] = 20 Check: 20 < 25 → So, search in the right half. Update range: low = 4 high = 7 mid = (4 + 7) / 2 = 5 → array [5] = 30 Check: 30 > 25 → So, search in the left half of this range. Update range: low = 4 high = 4 mid = (4 + 4) / 2 = 4 → array [4] = 25 Check: 25 == 25 Element found at index 4 Final Result: Target element 25 is found at index 4 Binary Sort Python code: function binarySearch(arr, target): low = 0 high = len(arr) - 1 while low <= high: mid = (low + high) // 2 if arr[mid] == target: return mid elif arr[mid] < target: low = mid + 1 else: high = mid - 1 return -1
Time Complexity
| Case | Time Complexity |
| Best Case | O (1) |
| Average | O (log n) |
| Worst Case | O (log n) |
- n = number of elements
Space Complexity
- O (1) for iterative version
- O (log n) for recursive version (stack space)
Important:
- Works only on sorted arrays
- Much faster than Linear Search for large data
