Heap Sort Algorithm
Heap Sort is a comparison-based sorting algorithm that uses a binary heap data structure (usually a max heap). It repeatedly removes the largest element from the heap and places it at the end of the array.
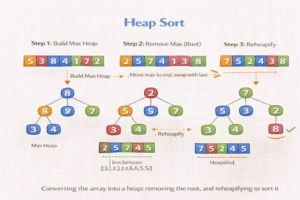
How Heap Sort Works (Step-by-Step)
- Build a Max Heap
- Convert the input array into a max heap.
- In a max heap, the largest element is at the root (index 0).
- Swap Root with Last Element
- Swap the first (largest) element with the last element of the array.
- Reduce Heap Size and Heapify
- Exclude the last element from the heap (it is now in correct position).
- Apply heapify to restore the max heap property.
- Repeat
- Continue the process until the heap size becomes 1.
Example of Heap Sort
Input Array:[5, 3, 8, 4, 1, 7, 2]
Step 1: Build Max Heap
Convert array into max heap:
→ [8, 4, 7, 3, 1, 5, 2]
Step 2: Swap Max (8) with Last (2)
Swap → [2, 4, 7, 3, 1, 5, 8]
Heapify remaining (ignore last sorted element):
→ [7, 4, 5, 3, 1, 2, 8]
Step 3: Swap Max (7) with Last Unsorted (2)
Swap → [2, 4, 5, 3, 1, 7, 8]
Heapify:
→ [5, 4, 2, 3, 1, 7, 8]
Step 4: Swap Max (5) with Last Unsorted (1)
Swap → [1, 4, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8]
Heapify:
→ [4, 3, 2, 1, 5, 7, 8]
Step 5: Swap Max (4) with Last Unsorted (1)
Swap → [1, 3, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8]
Heapify:
→ [3, 1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8]
Step 6: Swap Max (3) with Last Unsorted (2)
Swap → [2, 1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8]
Heapify:
→ [2, 1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8]
Step 7: Swap Remaining
Swap 2 and 1 →
Final Sorted Array →[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8]
Heap sort Python code:
public class HeapSort {
// Function to perform Heap Sort
public static void heapSort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
// Step 1: Build Max Heap
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(arr, n, i);
}
// Step 2: Extract elements from heap
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--) {
// Move current root to end
int temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
// Call heapify on reduced heap
heapify(arr, i, 0);
}
}
// Heapify subtree rooted at index i
public static void heapify(int[] arr, int n, int i) {
int largest = i; // Assume root is largest
int left = 2 * i + 1; // Left child
int right = 2 * i + 2; // Right child
// If left child is larger than root
if (left < n && arr[left] > arr[largest]) {
largest = left;
}
// If right child is larger than largest so far
if (right < n && arr[right] > arr[largest]) {
largest = right;
}
// If largest is not root
if (largest != i) {
int swap = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[largest];
arr[largest] = swap;
// Recursively heapify affected subtree
heapify(arr, n, largest);
}
}
// Function to print array
public static void printArray(int[] arr) {
for (int num : arr) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7};
System.out.println("Before Sorting:");
printArray(arr);
heapSort(arr);
System.out.println("After Sorting:");
printArray(arr);
}
}
Time Complexity
| Case | Time Complexity |
| Best Case | O (n log n) |
| Average | O (n log n) |
| Worst Case | O (n log n) |
- Heap sort is not stable.
- It is in-place (no extra space is used except for recursion/heapify).
Space Complexity
- O (1) — It’s an in-place sorting algorithm.
Use Case:
Heap Sort is useful when you need guaranteed O(n log n) performance and don’t mind losing stability.
